Modern Physics - Graduate level important notes for competitive exams - PART1
- Aston’s Mass Spectroscope enables identification of isotopes.
- Packing fraction (P) is mass defect for elementary particle, P = Mass defect/ Mass number.
- Negative Packing Fraction implies exceptional Nuclear Stability.
- Binding energy of Neutron is 2.23 MeV, Spin = 1.
- Binding energy of Lithium is 37.7 MeV. Binding energy per Nucleon is 37.7/7 = 5.4MeV.
- Diameter of Nucleus is of order of 10⁻¹⁴ m.
- Intensity of X- rays varies with current.
- The quality of X- rays is a function of Potential difference between Cathode and Anode.
- Moseley’s law is based on Bohr’s theory of atom.
- Wave length of X – rays ranges from 10⁻¹⁰ to 10⁻⁸ m.
- Speed of X- rays = 3*10⁸ m/sec.
- The short wave length of X- rays emitted from X- ray tube depends on current in tube.
- The operating Voltage in a typical X- ray tube is of order 10 KV.
- Stopping Potential is independent of intensity of incident Radiation.
- Saturation current is directly proportional to Intensity of Incident Radiation.
- Compton Effect is observed with X-Rays and Gamma Rays but not with Visible and UV Radiation.
- The constant factor of probability of transition is known as "Spontaneous Emission". It leads to broad Spectrum.
- The variable factor of probability of transition is known as "Stimulated Emission".
- Spontaneous emission was postulated by "Neil Bohr".
- Stimulated emission was postulated by "Einstein".
- Probable rate of occurrence of absorption transition from state 1 to state 2 depends on properties of two states and is proportional to energy density.
- Probability rate of "spontaneous emission" depends on properties of states but does not depend on energy density.
- In Ruby(Al2O3) LASER, Chromium ions(Cr3+) acts as "active" material.
- Ruby(Al2O3) LASER is a “pulsed" LASER . The output beams of it have principal wave length in visible spectrum.
- Gas LASER(He-Ne) is a continuous LASER with high Monochromaticity.
- In He– Ne LASER, Helium atoms are in majority while ‘Ne’ atoms are in minority.
- In He–Ne LASER, we observe emission between 5S to 3P.
- In He- Ne LASER, Helium gas serves as a mediator in producing Population Inversion.
- Bragg’s law is a result of “ Periodicity of Lattice Points”.
- Fine structure of H⍺ line includes 7 no. of valid transitions.
- X- ray emission is referred to as inverse photo electric effect.
- Ratio of Einstien's Spontaneous & stimulated coefficients = 8Πh𝝂³/C³.
- Spectrum of non- rigid diatomic molecule is similar to that of Rigid molecule except that each line is displaced slightly to lower frequency.
- Pure "Vibrational spectra" are observed only in liquids. Because interactions between neighboring molecules prevent this Rotational motion.
The Davisson-Germer Experiment
The experiment gave the evidence of wave nature possession by materialistic particle(electron) for the first time.
The arrangement of equipment used for the experiment is as follows
Now from Bragg’s equation for maxima in diffraction pattern for same energy electrons
The arrangement of equipment used for the experiment is as follows
Procedure:
An electron gun is used in order to produce electrons. The electrons so produced are accelerated by applying a high potential towards the target crystal, in this case the target crystal is nicker. The accelerated electron beam is made into fine beam by passing it through a Collimator ‘c’.
The crystal is mounted on an arrangement which could be rotated in different directions perpendicular to the plane of diagram.
The electrons are scattered in all directions by atomic planes of crystal.
The intensity of electron beam ( no. Of electrons) scattered in a particular direction is measured by electron collector which can be rotated about the same axis as target crystal.
The collector is connected to a sensitive Galvanometer whose deflection is proportional to intensity of electron beam entering collector . The electron collector is also called Faraday cylinder.
A retarding potential is applied to Faraday cylinder such that only fast electrons can reach it and secondary electrons emitted from crystals are stopped.
A graph is then plotted between galvanometer current against angle ‘θ' between incident beam and diffracted beam i.e, beam entering Faraday cylinder.
In the investigation , the electron beam accelerated by 54V and at an angle of 50 between incident and diffracted beam , a sharp maximum has occurred in electron distribution.
The crystal is mounted on an arrangement which could be rotated in different directions perpendicular to the plane of diagram.
The electrons are scattered in all directions by atomic planes of crystal.
The intensity of electron beam ( no. Of electrons) scattered in a particular direction is measured by electron collector which can be rotated about the same axis as target crystal.
The collector is connected to a sensitive Galvanometer whose deflection is proportional to intensity of electron beam entering collector . The electron collector is also called Faraday cylinder.
A retarding potential is applied to Faraday cylinder such that only fast electrons can reach it and secondary electrons emitted from crystals are stopped.
A graph is then plotted between galvanometer current against angle ‘θ' between incident beam and diffracted beam i.e, beam entering Faraday cylinder.
In the investigation , the electron beam accelerated by 54V and at an angle of 50 between incident and diffracted beam , a sharp maximum has occurred in electron distribution.
The incident beam and diffracted beam in this experiment make an angle of 65⁰ with Braggs plane.
For a 54 V electron , the de-broglie wavelength associated with the electron is given by
ƛ = 12.25/√V = 12.25/√54 A⁰ = 1.66 A⁰
ƛ = 12.25/√V = 12.25/√54 A⁰ = 1.66 A⁰
Now from Bragg’s equation for maxima in diffraction pattern for same energy electrons
2d sinθ' = nƛ; 2*0.91*10^-10*sin 65⁰ = 1*ƛ;
ƛ = 1.65 A⁰
Thus, both theoretical and experimental values are in excellent agreement.
Thus Davission - Germer experiment provides a direct verification of de-broglie hypothesis of wave nature of moving particles.
Thus, both theoretical and experimental values are in excellent agreement.
Thus Davission - Germer experiment provides a direct verification of de-broglie hypothesis of wave nature of moving particles.
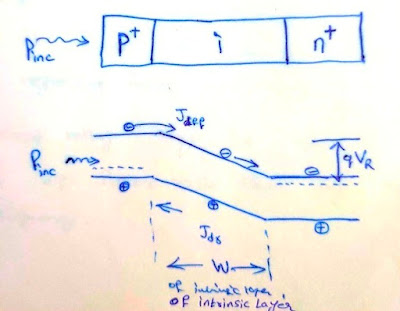
PIN Diode - General Description
It is a junction photo diode.
Basic principle :- The diode is operated under reverse biased condition. Under photo excitation , photons are absorbed mainly in depletion region and also in neutral region , particularly on top where light is incident. the absorbed photons create e-h pairs
They give rise to photo current , the magnitude of which depends on quantum efficiency.
so photo excitation is therefore detected as an increase in reverse biased current of a junction photo diode.
Large depletion layer may increase no.of e-h pairs generated but it consequently increases response time of diode degrading its high speed performance.
Pin diodes have no internal gain but can have very large band widths.
They give rise to photo current , the magnitude of which depends on quantum efficiency.
so photo excitation is therefore detected as an increase in reverse biased current of a junction photo diode.
Large depletion layer may increase no.of e-h pairs generated but it consequently increases response time of diode degrading its high speed performance.
Pin diodes have no internal gain but can have very large band widths.
Since dark current in a reverse biased junction is very small , pin diode is more sensitive device than a photo conductor.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)